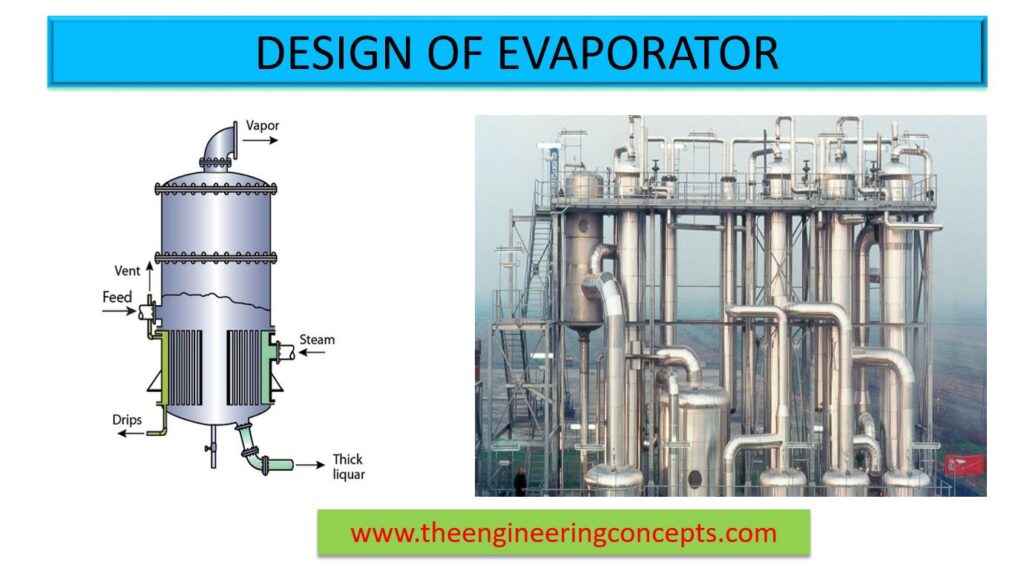
What is an evaporator ?
An evaporator is a device, majorly a type of heat exchanger, used in an industrial process to separate the liquid, mainly water, from a chemical compound into gas or water vapor. Evaporators are commonly used in food industry to concentrate the food by evaporating the water content from the food.
How does an evaporator work?
At first, the chemical compound is fed to the evaporator. It then passes across a heat source that the compound into a gaseous form (vapor). After this, the remaining part of the compound is condensed and fed into a second evaporator if it is a multi-effect evaporator system. If it is a single evaporator system, the condensate (condensed material) is removed.
Applications of evaporators:
Evaporators are used in several industries likes:
- Food
- Pharmaceutical
- Petrochemical
- paper and pulp
- Waste Management
- Textile
Types of evaporators :
There are several types of evaporators available in the market; depending on their use, we can choose from the comprehensive list mentioned below.
- Natural / Forced circulation evaporator
- Falling film evaporator
- Rising film (Long Tube Vertical) evaporator
- Short Tube evaporator
- Climbing and falling-film plate evaporator
- Multiple- effect evaporator
- Agitated thin-film evaporator
- Vertical short tube evaporator
- Kettle evaporator
- Scraped/ Wide surface evaporator
- Centri therm evaporator
- Gasketed Plate Evaporator
- Robert type natural circulation evaporator
- Flash evaporators
- Compact evaporator
Factors to be considered while designing an evaporator:
1. Thermal Considerations :
- Tube size, tube arrangement, and tube materials: The tube diameter, tube arrangement, and tube length are determined by trial and error calculations whereas, the tube materials are selected based on the corrosiveness of the compound and working situations.
- Heat transfer coefficients: The heat transfer coefficient on the shell side usually is very high compared to the liquid side. The later heat transfer coefficient controls the rate of heat transfer. The overall coefficient is calculated from the performance data of an operating evaporator of the same type and processing the same solution.
- Boiling point elevation (BPE): When the boiling point of the concentrated liquor is higher than that of pure solvent (or water), it is known as boiling point elevation (BPE). Boiling point of a solvent is higher when other component is added. BPE (Boiling Point Elevation ) occurs because the vapor pressure is less than that of the pure solvent at the same temperature.
Note : Selection of suitable evaporator: The selection of the most suitable evaporator type depends on several factors. Mainly these are: (i) throughput, (ii) viscosity of the solution (and its increase during evaporation), (iii) nature of the product and solvent (such as heat sensitivity and corrosiveness), (iv) fouling characteristics and, (v) foaming characteristics.
2. Mechanical Considerations:
- Operating temperature and pressure: The operating temperature is the temperature that is maintained for the specified operation of the metal vessel suitably selected during design.
- Operating Pressure : The operating pressure is the pressure at the top of the vessel at which it normally operates. It should be lower than design pressure or set pressure of any pressure relieving device.
- Design temperature and pressure: The design pressure is generally is the sum of the maximum allowable pressure and the static head of the fluid in the pressure vessel. The design temperature is the temperature which corresponds to design pressure.
- Maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP): The maximum allowable working pressure is the maximum pressure to which the equipment can be safely operated. The MAWP for a vessel is the maximum permissible pressure at the top of the vessel in its normal operating position at a specific temperature, usually the design temperature.
- Thermal expansion: Thermal expansion between various parts of equipment has a significant effect on the mechanical design. Thermal expansion may also determine how tubes are fixed to the tube sheet.
Assumptions for designing an evaporator:
- Specific heat of feed is constant for all temperatures and concentrations.
- Overall heat transfer coefficient remains constant through the operation of the evaporator.
- The evaporator is operated at a steady state.
- Vapors from each effect are solute-free.
- Heat transfer area is nearly equal for each effect
Steps in the calculation of evaporator design:
The below-mentioned calculations are for a Natural Circulation evaporator
1. The number of tubes (N):
Number of tubes = Heating surface / π x Mean Diameter x Effective Length
where,
- Effective Length of the tube ( L ) = Tube length – 2(Tube plate thickness)- 2(Tube expansion allowance)
2. Tube plate & Downtake diameter:
The area which is occupied for tubes in tube plate :
Tube plate area required for tubes only (AT) = (0.866 x Tube Pitch2 x No. of Tubes / Proportional factor)* %extra
where as:
- Tube Pitch (P) = Outer Diameter of the tube + Legment of the tube + tube clearance + hole clearance
3. Diameter of the down take:
- Diameter of the single downtake = Tube plate dia for tubes * % of downtake on tube plate.
- Diameter of the central downtake in multiple down takes design = √ [(Area of the single downtake – Total area of peripheral down takes) x 4/π)].
The final required tube plate diameter:
Final Diameter of the tube plate = √ [(Area of the Tube plate for tubes + Downtake area) x 4/π)]
4. Diameter required for vapor inlet & Diameter of the Calendria in radial steam/vapor entry
- Diameter of the Vapour Inlet:
Diameter of each steam entry = √ [(Area required for the vapor entry / Number of vapour entries) x (4/π)]
- Calendria diameter at the entry of the steam
Diameter of calendria at the point of radial steam entry = Final Diameter of the tube plate + Width of the steam entry.
5. Vapour outlet pipe diameter:
Vapour outlet pipe diameter in metres = √ [vapour volume / (0.785 x velocity of vapour)]
6. Diameter of the condensate line:
Diameter of each condensate line = √ (Volume of the condensate each./(0.785 x velocity of condensate)).
7. Noxious gases connections:
Diameter of each non condensable gases line = √ (Total area of non-condensable gases /0.785*no. of points)
8. Calendria shell thickness:
Calendria shell thickness in mm = (Maximum allowable pressure * ID of the Calendria / (2* Allowable stress * Welding Joint efficiency – Maximum allowable pressure)) + corrosion allowance
9. Vapour shell thickness:
Vapour shell thickness = (Maximum allowable pressure * ID of the Calendria / (2* Allowable stress * Welding Joint efficiency – Maximum allowable pressure i)) + corrosion allowance.
10. Tube plate thickness:
Tube plate thickness in mm = √ (K / (2 + 3K))x ID of the shell x √((0.25 x Maximum allowable pressure)/ Allowable stress) + corrosion allowance
Article Written By : Shravani Kharote
Article Sources : Sugar Process Technology; Academia; AMU; CIVIDAC
Also Read:
PROCESS CONTROLLERS AND ITS TYPES
Liquid Level Flow Control Loop
Heat Exchanger Temperature Control
Piping and Instrumentation Diagram – P&ID
How to choose betwwen PLC and DCS systems for process industries ?
What is the Difference Between HMI and SCADA?
What is SCADA ? How does SCADA Works?
What is Programmable Logic Controller / PLC ?