Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a process of thermal conversion of organic materials into volatile products containing hydrocarbons, liquid and gases and solid residue as ash and carbon in the absence of oxygen i.e. inert atmosphere. The industrial pyrolysis takes place at higher level temperatures, while in small scale operations the temperature scale is lower. Pyrolysis is also known as first step in gasification.
Aricle written By : Pallavi Wankhede
Working of Pyrolysis for Bio-oil Production:
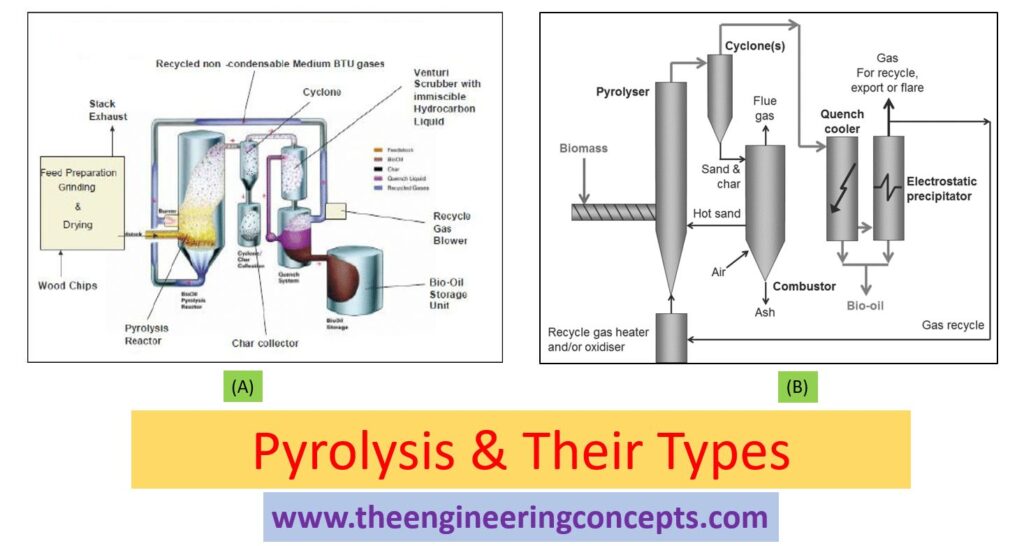
- Initially all biomass or feedstock materials will be prepared for the pyrolysis process by drying, cutting operations. Once the feedstock is completely dried and formed into smaller pieces, it is then passed through the pyrolysis reactor.
- The pyrolysis reactor works in the absence of oxygen and the combustion chamber will indirectly give the heat to the reactor.
- During this process, some ash particles will be created from the feedstock and further it will be collected in the ash chamber.
- The gas will be liberated (get free) from the biomass and will reach to the cyclone which rotate the gas and helps to collect the char particles in the char collector.
- After that, the gas in cyclone will be passed through the quencher where the gas will get combined with water. This combination will later produce bio-oil and it will be collected in the bio-oil collector. The remaining gas from the quencher will be taken out and reused in the combustion chamber.
Types of Pyrolysis:
Based on temperature range and processing time, pyrolysis is classified into three types:
- Slow Pyrolysis: It involves lengthy solids and gases, slow biomass heating rate and low temperature ranges in between 0.2 to 30C and the highest temperature could be up to 5000 . Slow pyrolysis is used to produce tar and char as main product while biomass can be devolatilized slowly.
- Flash Pyrolysis: It takes place at very rapid heating rates and temperatures range in between 4000C to 6000 . The residence time of this process is very low as 2seconds. It gives gas and tar in fewer amounts as compared to slow pyrolysis.
3. Fast Pyrolysis: It is most commonly used to produce bio-oil and gas. The temperature range for fast pyrolysis is in between 6000C to 10000 The biomass is heated in between this temperature range until the desired amount of bio-oil and gas is produced. On the other hand, it accumulates large amount of char which needs to be removed frequently to avoid process disturbance due to accumulation inside the pyrolizer.
- Apart from all these, the maximum yield of bio-oil from the thermal decomposition of biomass can be increased up to 81 % (dry weigh basis) with the help of proper choice in heating rate, temperature range and the evacuation of product from the reaction zone.
- For an instance: A slower heating rate, lower pyrolysis temperature and longer residence time can maximize the yield of solid char.
- A higher heating rate, higher pyrolysis temperature and shorter residence time can maximize the yield of gas obtained.
- A higher heating rate, an intermediate pyrolysis temperature and shorter residence time can maximize the yield of liquid.
Pyrolyzer :
The reactor used for pyrolysis process is often called as pyrolizer. Depending on the product requirement and feed conditions, the type of pyrolizer can be selected.
1. Bubbling Fluidized Bed Pyrolizer :
- This type of pyrolizer is easy to construct and design as compared to other types of pyrolizer. These provides large heat storage capacity, better temperature control and heat transfer characteristics.
- It also provides better gas-solid contact.
- In this pyrolizer, the fluidizing gas flow rate controls the residence time of vapor and solids.
- During reaction, the char formed in the pyrolizer act as catalyst in the cracking vapors. Once the cracking is done, the char is collected with the help of entrainment process.
2. Circulating Fluidized Bed / Transported Bed Pyrolizer:
- Circulating fluid bed has similar characteristics as that of bubbling fluidized bed excluding the residence time of vapor and char that are very high in this type due to higher gas velocities.
- This pyrolizer is popular for large scale combustion operations.
- This type of pyrolizer provides better gas-solid contact and high processing capacity. It uses the entire height of the vessels for gas solid contacting.
- It also has potential to deal with cohesive solids as compared to bubbling fluidized bed.
3. Ablative Pyrolizer:
- This type of pyrolizer is designed to soften the feedstock transferred from hot reactor wall under pressure.
- Also, it is used to decompose large feedstock particles into smaller one as the reaction rates are not influenced by biomass particles.
- This type of pyrolizer provides high relative motion between reactor wall and the particles in presence of high pressure exerted by the particles of the hot reactor wall.
- There is no need to provide inert gases as the reaction rate is more intense due to high relative motion. Thus, its processing equipment is small.
Selection and Efficiency of Pyrolysis:
- Pyrolysis is most commonly used in chemical industry due to its simple and inexpensive way of operation. It is used for the conversion of waste feedstocks which helps to reduce the filling of waste materials to land.
- It also helps to reduce greenhouse gas emission, water pollution due to waste material conversion and not adding directly to water bodies like river, lake.
- On the other hand, the construction of power plant for pyrolysis is very rapid process.
- Pyrolysis is used to get products like methanol, char, activated carbon and other substances from wood.
- Pyrolysis can also be used in cooking processes like caramelizing, grilling, frying and baking.
- While designing a pyrolizer, the heat transfer is a major consideration.
- The heat balance for a typical pyrolizer can be written as:
Content Source: ScienceDirect; Wikipedia
Image Source: ResearchGate
Read Also :
Thermodynamic Cycle
Fluid Coking
Types of Control System
What is Thermowell ? Types of Thermowell
Factors Affecting The Operation Of Distillation Column
Pump Selection Criteria
Piping and Instrumentation Diagram – P&ID
How to choose betwwen PLC and DCS systems for process industries ?
Cement Manufacturing Process
Vinyl Chloride from Ethylene
Cooling Tower
Psychrometric Chart
What is Boiler ?
Venturi Flow Meter
Pitot Tube
Coriolis Mass Flow Meter
RECIPROCATING PUMP
Design of Centrifugal Pump
Valve & Its Types
Cavitation
P&ID Symbols and Notation
What is the Difference Between HMI and SCADA?
What is SCADA ? How does SCADA Works?
What is Programmable Logic Controller / PLC ?
What is Distributed Control Systems (DCS) ?
Heat Exchanger Temperature Control
What is Compressor Surge ?
Ejectors & Its Working Principle
Desuperheater
Three Phase Seperator