Thermocompressor
Introduction:
Steam is the common source of heat in most of the process industries. This steam is mainly produced from fossils and are fast depleting in nature. The generation cost of steam is also increasing drastically day by day. It is therefore an impressive that the process industries focus on steam utilization and initial action to minimize or optimize the use of steam.
Aricle written By : Rayyan Shaikh
One of the Direct ways of reducing steam consumption is to maximize the use of low pressure flash steam. Thermocompressor offer an energy efficient solution to recover or reclaim low grade or low pressure steam.
A large number of industries vent low pressure steam to the atmosphere as this steam is at low temperatures and therefore can not be useful redeployed in the process. However with thermocompressor technology one can very easily increase the pressure and temperature of flash steam. As a consequence energy consumption reduces by a significant amount.
What is Thermocompressor ?
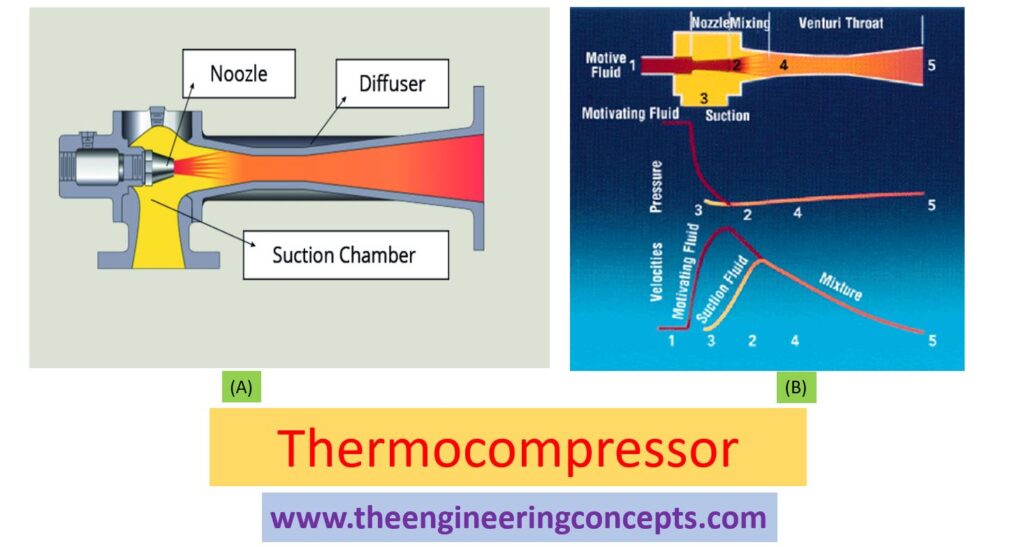
Thermocompressor is a fluid jet device that compresses the low pressure steam resulting to a high pressure steam by using the principle of energy conservation. High pressure motive steam is passed with supersonic speeds through a converging diverging nozzle where it meets the slow moving low pressure steam (through suction inlet) resulting entrainment and mixing. This mixed jet is then allow to pass through a diffuser (where due to geometry velocity decreases results in increase in pressure energy as per Bernoulli’s principle) at which the kinetic energy is converted into pressure energy. Thus the discharged steam, which having comparatively higher pressure energy is again put back back into the process for more higher pressure.
The name thermocompressor is derived from the process of using thermal energy or enthalpy of steam to achieve compression.
So Simply thermocompressor is a device which is used to reuse low pressure steam and get it to converted into high pressure steam as a result, reduces capital cost of company by reducing the consumption.
CONSTRUCTION
Thermocompressor consist of the main parts.
- Nozzle
- Suction chamber
- Mixing Chamber
- Diffuser
Thermocompressor have three connection.
- The high pressure steam that enter in the nozzle called motive steam.
- The flash steam or LP(low pressure) steam that is recoverd/compressed is know as the suction steam
- The resultant steam that exits the thermocompressor from the diffuser is termed as the discharge steam.
At first the motive steam comes into the suction chamber at very high speed. This create low pressure zone in control chamber cause of this low pressure steam or flash steam is sucked in suction chamber. Both steam mixes together in the mixing chamber and allow to flow through diffuser, where the velocity falls and pressure rises. As a result intermediate pressure steam is obtained.
Working :
- High pressure steam called motive steam in expand in the nozzle-process 1-2, this being a isentropic (entropy =constant) process.
- Due to frictional losses in the middle the actual process of expansion achieved is represented by process 1-2′.
- The high velocity of motive steam after the nozzle entertains the low pressure steam ( suction steam).
- Process 2′-4 and 3-4 represent the mixing process of the motive steam and entrained suction steam.
- Process 4-5 represents the process in the diffuser.
- Velocity head of the mixture is converted to pressure head in the diffuser.
- Due to frictional losses the actual process Achieved is 4-5′.
ADVANTAGES OF BOOSTING STEAM USING THERMOCOMPRESSOR.
- No condensation losses take place
- Thermal efficiency of system is extremely high
- Entrainment of low pressure steam results in substantial saving
- No moving parts results minimal maintenance cost
- No major operational charges
- Compact in Size
- Insensitive to fouling
- High operational reliability
- Low investment.
Applications
- Thermocompressor has a wide potential scope from industrial view point.
- When ever low pressure steam is being vented or being condensate, thermocompressor can be used.
- Paper industry, solvent extraction plant, tobacco plant textiles, rayon, rubber , sugar dairy, refinery, chemical plants, flash steam recovery, distillery , cogeneration plant.
Content source : Inveno; Wikipedia
Image source : Inveno
Read Also :
Thermodynamic Cycle
Fluid Coking
Types of Control System
What is Thermowell ? Types of Thermowell
Factors Affecting The Operation Of Distillation Column
Pump Selection Criteria
Piping and Instrumentation Diagram – P&ID
How to choose betwwen PLC and DCS systems for process industries ?
Cement Manufacturing Process
Vinyl Chloride from Ethylene
Cooling Tower
Psychrometric Chart
What is Boiler ?
Venturi Flow Meter
Pitot Tube
Coriolis Mass Flow Meter
RECIPROCATING PUMP
Design of Centrifugal Pump
Valve & Its Types
Cavitation
P&ID Symbols and Notation
What is the Difference Between HMI and SCADA?
What is SCADA ? How does SCADA Works?
What is Programmable Logic Controller / PLC ?
What is Distributed Control Systems (DCS) ?
Heat Exchanger Temperature Control
What is Compressor Surge ?
Ejectors & Its Working Principle
Desuperheater
Three Phase Seperator